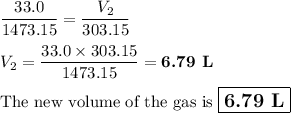Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
The pressure is constant, so, to calculate the volume, we can use Charles' Law.
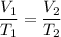
Data:
V₁ = 3300 L; T₁ = 1200.0 °C
V₂ = ?; T₂ = 30 °C
Calculations:
(a) Convert temperatures to kelvins
T₁ = (1200.0 + 273.15) K = 1473.15 K
T₂ = (30 + 273.15) K = 303.15 K
(b) Calculate the new volume