Answer : The value of
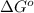 across the membrane is 6.80 kJ/mol
across the membrane is 6.80 kJ/mol
Explanation :
The relation between the equilibrium constant and standard Gibbs free energy is:
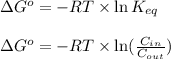
where,
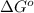 = standard Gibbs free energy = ?
= standard Gibbs free energy = ?
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/K.mol
T = temperature =
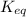 = equilibrium constant
= equilibrium constant
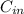 = concentration inside the cell =
= concentration inside the cell =
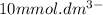
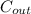 = concentration outside the cell =
= concentration outside the cell =
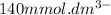
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
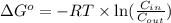
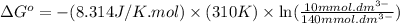
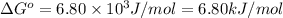
Thus, the value of
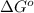 across the membrane is 6.80 kJ/mol
across the membrane is 6.80 kJ/mol