Step-by-step explanation:
Common ion effect is defined as the effect which occurs on equilibrium when a common ion (an ion which is already present in the solution) is added to a solution. This effect generally decreases the solubility of a solute.
Equilibrium reaction of strontium sulfate and sodium sulfate follows the equation:
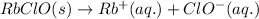
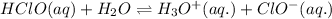
According to Le-Chateliers principle: If there is any change in the variables of the reaction, the equilibrium will shift in the direction in order to minimize the effect.
In the equilibrium reactions, hypochlorite ion is getting increased on the product side, so the equilibrium will shift in the direction to minimize this effect, which is in the direction of hydrogen hypochlorite.
Thus, the addition hypochlorite ions will shift the equilibrium in the left direction.
The dissociation of hydrogen hypochlorite is suppressed due to the common ion effect.