Answer: The moles of carbon dioxide produced is 0.00095 moles
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
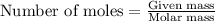
Given mass of glucose = 1.02 g
Molar mass of glucose = 180.16 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
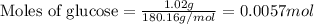
To calculate the number of moles, we use ideal gas equation:
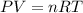
where,
P = pressure of the gas = 0.970 atm
V = Volume of the gas = 25 mL = 0.025 L (Conversion factor: 1 L = 1000 mL)
T = Temperature of the gas =
![37^oC=[37+273]K=310K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/g4qi44srgtaq7fmv4dze4d1dxww2knro75.png)
R = Gas constant =
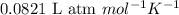
n = number of moles of oxygen gas = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
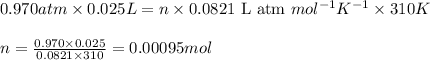
The chemical equation for the combustion of glucose follows:
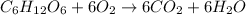
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
6 moles of oxygen gas reacts with 1 mole of glucose
So, 0.00095 moles of oxygen gas will react with =
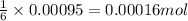 of glucose
of glucose
As, given amount of glucose is more than the required amount. So, it is considered as an excess reagent.
Thus, oxygen gas is considered as a limiting reagent because it limits the formation of product.
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
6 moles of oxygen gas produces 6 moles of carbon dioxide
So, 0.00095 moles of oxygen gas will produce =
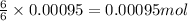 of carbon dioxide
of carbon dioxide
Hence, the moles of carbon dioxide produced is 0.00095 moles