Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Net force acting on the electron,
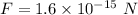
Displacement, d = 5 cm = 0.05 m
(a) Let
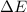 is the change in kinetic energy of the electron. It can be calculated using work energy theorem. Mathematically, it is given by :
is the change in kinetic energy of the electron. It can be calculated using work energy theorem. Mathematically, it is given by :
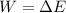
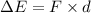
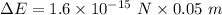
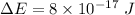
(b) Initial speed of the electron, u = 0
Again using the work energy theorem as :
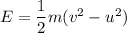
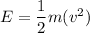
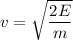
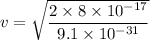

Hence, this is the required solution.