Answer : The the rate expression will be:
![Rate=-(d[Cl_2])/(dt)=-(1)/(3)(d[F_2])/(dt)=+(1)/(2)(d[ClF_3])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/4bomnq62k2pzvrzo1cbhxbe18rvrlrw8yo.png)
Explanation :
The general rate of reaction is,
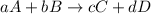
Rate of reaction : It is defined as the change in the concentration of any one of the reactants or products per unit time.
The expression for rate of reaction will be :
![\text{Rate of disappearance of A}=-(1)/(a)(d[A])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/krw50w9jsmh85qkkika6f5x5tpfm9u2j5r.png)
![\text{Rate of disappearance of B}=-(1)/(b)(d[B])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/40zbnj8t8l3ih5v1ai01k3jinay9t3oaz9.png)
![\text{Rate of formation of C}=+(1)/(c)(d[C])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/3i2ex56t5d4z5ocfpxi07khq250ilg4c97.png)
![\text{Rate of formation of D}=+(1)/(d)(d[D])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/1q3dcgf0p1iydqns4peo4rla4tgg7d4w6b.png)
![Rate=-(1)/(a)(d[A])/(dt)=-(1)/(b)(d[B])/(dt)=+(1)/(c)(d[C])/(dt)=+(1)/(d)(d[D])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ezf5j0xrg9bky8ghn9466rck1gxg8xn5gq.png)
From this we conclude that,
In the rate of reaction, A and B are the reactants and C and D are the products.
a, b, c and d are the stoichiometric coefficient of A, B, C and D respectively.
The negative sign along with the reactant terms is used simply to show that the concentration of the reactant is decreasing and positive sign along with the product terms is used simply to show that the concentration of the product is increasing.
Now we have to determine the rate expressions for this given reaction.
The given balanced equations is:
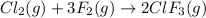
![\text{Rate of disappearance of }Cl_2=-(d[Cl_2])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/eypdu7fqxs72kt43212l4hwrgqw0sh6gge.png)
![\text{Rate of disappearance of }F_2=-(1)/(3)(d[F_2])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/leari0u3uj9l98zgmlb6cph7k7scf7uwwy.png)
![\text{Rate of formation of }ClF_3=+(1)/(2)(d[ClF_3])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/4ihnkwdzzgdeq7z9k20rm6g6elmxpxi62i.png)
Thus, the rate expression will be:
![Rate=-(d[Cl_2])/(dt)=-(1)/(3)(d[F_2])/(dt)=+(1)/(2)(d[ClF_3])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/4bomnq62k2pzvrzo1cbhxbe18rvrlrw8yo.png)