Answer:
The claim that he rate of inaccurate orders is equal to 10% is supported by statistical evidnece at 5% level
Explanation:
Given that in a study of the accuracy of fast food drive-through orders, one restaurant had 34 orders that were not accurate among 371 orders observed.
Sample proportion
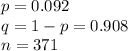
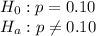
(Two tailed test at 5% significance level)
p difference =
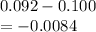
Std error if H0 is true =
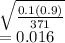
Test statistic Z = p diff/std error
=0.539
p value = 0.5899
Since p > 0.05 accept null hypothesis
The claim that he rate of inaccurate orders is equal to 10% is supported by statistical evidnece at 5% level