Answer:
1.27 atm is the final pressure of the oxygen in the flask (with the stopcock closed).
2.6592 grams of oxygen remain in the flask.
Step-by-step explanation:
Volume of the flask remains constant = V = 2.0 L
Initial pressure of the oxygen gas =
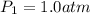
Initial temperature of the oxygen gas =
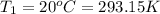
Final pressure of the oxygen gas =
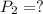
Final temperature of the oxygen gas =
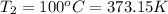
Using Gay Lussac's law:
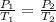
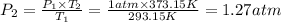
1.27 atm is the final pressure of the oxygen in the flask (with the stopcock closed).
Moles of oxygen gas = n
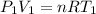 (ideal gas equation)
(ideal gas equation)
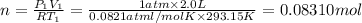
Mass of 0.08310 moles of oxygen gas:
0.08310 mol × 32 g/mol = 2.6592 g
2.6592 grams of oxygen remain in the flask.