Answer: 36.2 ml
Step-by-step explanation:
Assmed values :
weight of sulphurous acid = 0.104 g
volume of flask = 250 ml
Molarity of NaOH solution = 0.0700 M
Molarity of a solution is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved per Liter of the solution.
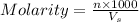
where,
n= moles of solute =
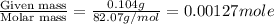
 = volume of solution in ml
= volume of solution in ml

According to the neutralization law,
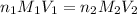
where,
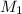 = molarity of
= molarity of
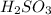 solution = 0.00507 M
solution = 0.00507 M
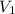 = volume of
= volume of
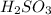 solution = 250 ml
solution = 250 ml
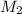 = molarity of
= molarity of
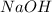 solution = 0.0700 M
solution = 0.0700 M
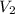 = volume of
= volume of
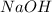 solution = ?
solution = ?
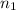 = valency of
= valency of
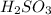 = 2
= 2
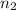 = valency of
= valency of
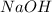 = 1
= 1
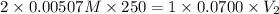
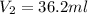
Therefore, the volume of solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point is 36.2 ml