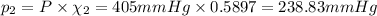Step-by-step explanation:
Part A:
Total pressure of the mixture = P = 5.40 atm
Volume of the container = V = 10.0 L
Temperature of the mixture = T = 23°C = 296.15 K
Total number of moles of gases = n
PV = nRT (ideal gas equation)
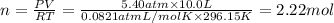
Moles of methane gas =
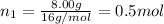
Moles of ethane gas =
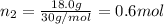
Moles of propane gas =
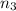
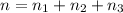
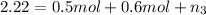
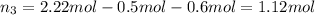
Mole fraction of methane =
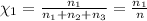
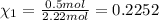
Similarly, mole fraction of ethane and propane :
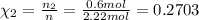
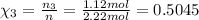
Partial pressure of each gas can be calculated by the help of Dalton's' law:
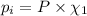
Partial pressure of methane gas:
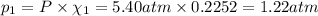
Partial pressure of ethane gas:
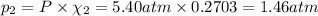
Partial pressure of propane gas:
Part B:
Suppose in 100 grams mixture of nitrogen and oxygen gas.
Percentage of nitrogen = 37.8 %
Mass of nitrogen in 100 g mixture = 37.8 g
Mass of oxygen gas = 100 g - 37.8 g = 62.2 g
Moles of nitrogen gas =
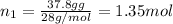
Moles of oxygen gas =
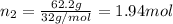
Mole fraction of nitrogen=
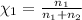
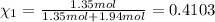
Similarly, mole fraction of oxygen
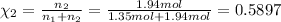
Partial pressure of each gas can be calculated by the help of Dalton's' law:
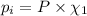
The total pressure is 405 mmHg.
P = 405 mmHg
Partial pressure of nitrogen gas:
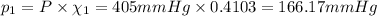
Partial pressure of oxygen gas: