Step-by-step explanation:
Let us assume that the ratio for the given reaction is 1:1.
Therefore, we will calculate the moles of
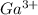 as follows.
as follows.
Moles of
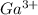 solution = molarity × volume (L)
solution = molarity × volume (L)
= 0.0440 M × 0.014 L
= 0.000616 moles
Moles of excess EDTA = 0.000616 moles
Also, the initial moles of EDTA will be calculated as follows.
Total initial moles of EDTA = 0.0600 M × 0.025 L
= 0.0015
Therefore, moles of EDTA reacted with
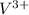 will be as follows.
will be as follows.
= 0.0015 - 0.000616
= 0.00088 moles
Since, we have supposed a 1 : 1 ratio between
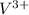 and EDTA .
and EDTA .
So, moles of
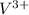 = 0.00088 moles
= 0.00088 moles
Now, we will calculate the molarity of
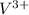 as follows.
as follows.
Molarity of
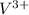 solution =
solution =
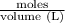
=
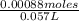
= 0.015 M
Thus, we can conclude that the original concentration of the
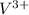 solution is 0.015 M.
solution is 0.015 M.