Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that 1.26 g of
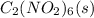 is placed in a
is placed in a
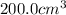 vessel.
vessel.
The balanced equation for the given reaction will be as follows.
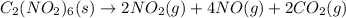 , \Delta H_{rxn}[/tex] = -455.66 kJ
, \Delta H_{rxn}[/tex] = -455.66 kJ
Now,
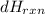 for 1.26g
for 1.26g
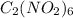 will be as follows.
will be as follows.
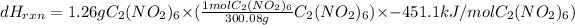
= -1.895 kJ
Now, we will calculate the moles of
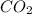 , NO and [/tex]NO_2[/tex] formed as follows.
, NO and [/tex]NO_2[/tex] formed as follows.
- Moles of
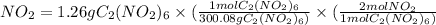
= 0.008398 mol
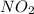
- Moles of NO =
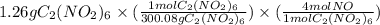
= 0.01680 mol NO
- Moles
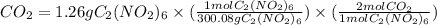
= 0.008398 mol
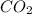
According to energy balance, we assume the same final temperature, assuming we heat the mix to
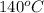 to make the reaction occur.
to make the reaction occur.
Then, calculate heat as follows.
Heat =
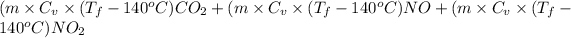
1895 J =
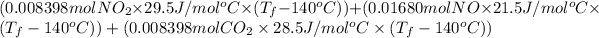
1895 =
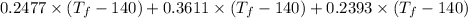
On rearranging the above equation we will calculate the final temperature as follows.
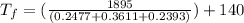
=
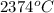
= 2647 K
According to the ideal gas equation, PV = nRT.
So, calculate the pressure as follows.
P =
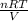
=
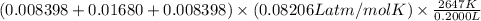
= 36.5 atm
Thus, we can conclude that the pressure of the mixture of gases after detonation is 36.5 atm.