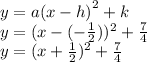Answer:
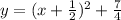
Explanation:
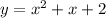
We can covert the standard form into the vertex form by either using the formula, completing the square or with calculus.
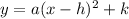
The following equation above is the vertex form of Quadratic Function.
Vertex — Formula
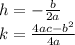
We substitute the value of these terms from the standard form.
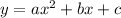
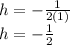
Our h is - 1/2
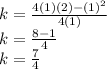
Our k is 7/4.
Vertex — Calculus
We can use differential or derivative to find the vertex as well.
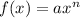
Therefore our derivative of f(x) —
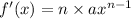
From the standard form of the given equation.
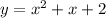
Differentiate the following equation. We can use the dy/dx symbol instead of f'(x) or y'
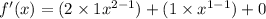
Any constants that are differentiated will automatically become 0.
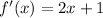
Then we substitute f'(x) = 0
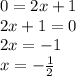
Because x = h. Therefore, h = - 1/2
Then substitute x = -1/2 in the function (not differentiated function)
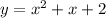
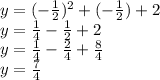
Because y = k. Our k is 7/4.
From the vertex form, our vertex is at (h,k)
Therefore, substitute h = -1/2 and k = 7/4 in the equation.