Answer:
Vertical asymptote:

Horizontal asymptote:
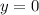 or x axis.
or x axis.
Explanation:
The rational function is given as:
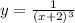
Vertical asymptotes are those values of
 for which the function is undefined or the graph moves towards infinity.
for which the function is undefined or the graph moves towards infinity.
For a rational function, the vertical asymptotes can be determined by equating the denominator equal to zero and finding the values of
 .
.
Here, the denominator is
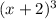
Setting the denominator equal to zero, we get
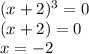
Therefore, the vertical asymptote occur at
 .
.
Horizontal asymptotes are the horizontal lines when
 tends towards infinity.
tends towards infinity.
For a rational function, if the degree of numerator is less than that of the denominator, then the horizontal asymptote is given as
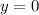 .
.
Here, there is no
 term in the numerator. So, degree is 0. The degree of the denominator is 3. So, the degree of numerator is less than that of denominator.
term in the numerator. So, degree is 0. The degree of the denominator is 3. So, the degree of numerator is less than that of denominator.
Therefore, the horizontal asymptote is at
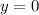 or x axis.
or x axis.