Stoichiometry is “quantitative relationship” among the “reactants” and the “products” in a “chemical reaction”.
Step-by-step explanation:
In stoichiometry “stoicheion” means element and “metron” means measure in Greek. The stoichiometric calculation depends upon “stoichiometric coefficients” in a “chemical equation” which can be explained as the “number of moles” of each substance (reactants or products). Stoichiometric calculation is done as follows:
For example reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen to form ammonia as
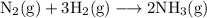
Here stoichiometric coefficients show that “one molecule of nitrogen” reacts with “three molecules of hydrogen” to form “two molecules of ammonia”. Multiplying Avogadro number
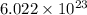 to no of molecules in equation:
to no of molecules in equation:
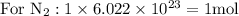
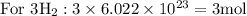
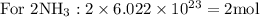
Taking molar masses into consideration:
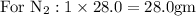
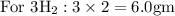
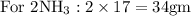
Hence balanced equation gives stoichiometric coefficients which gives proportion by moles.