Answer:
The angles of the ΔABC are:
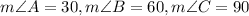
AB= 14 ft
Explanation:
Given:
A triangle ABC, with
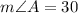 °
°
AB = 2MC
M is the mid-point of AB.
Let AB =
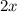
Therefore, AM = MB =
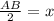
Also, MC =
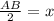
∴ AM = MB = MC =

Now, consider triangle AMC,
∵ AM = MC
∴
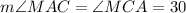 ° (
° (
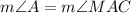 )
)
Now, exterior angle BMC is given as the sum of opposite interior angles of triangle AMC.
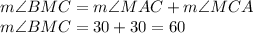
Consider triangle BMC,
∵ MB = MC
∴
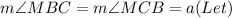
The sum of all interior angles is equal to 180°.
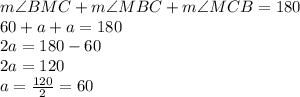
Therefore,
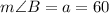 °
°
Also,
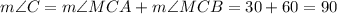 °
°
Therefore, the triangle ABC is a special right angled triangle with measures 30° - 60° - 90°.
For a special right angled triangle 30° - 60° - 90°, the hypotenuse is twice the base.
Here, AB is the hypotenuse and BC is the base. So,
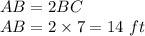
Therefore, AB = 14 ft.