Answer:
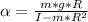
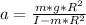
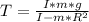
Step-by-step explanation:
By analyzing the torque on the wheel we get:
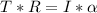 Solving for T:
Solving for T:
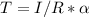
On the object:
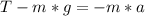 Replacing our previous value for T:
Replacing our previous value for T:
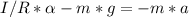
The relation between angular and linear acceleration is:
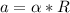
So,
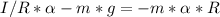
Solving for α:
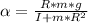
The linear acceleration will be:
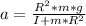
And finally, the tension will be:
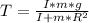
These are the values of all the variables: α, a, T