Answer:
(a) ΔG° = -474 kJ/mol; E° = 1.23 V
(b) ΔH° negative; ΔS° negative
(c) Since ΔS is negative, as T increases, ΔG becomes more positive. Therefore, the maximum work obtained will decrease as T increases.
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's consider the following reaction.
2 H₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2 H₂O(l)
with an equilibrium constant K = 1.34 × 10⁸³
(a) Calculate E° and ΔG° at 298 K for the fuel-cell reaction.
We can calculate the standard Gibbs free energy (ΔG°) using the following expression:
ΔG° = - R × T × lnK
ΔG° = - 8.314 × 10⁻³ kJ . mol⁻¹.K⁻¹ × 298 K × ln 1.34 × 10⁸³ = -474 kJ/mol
To calculate the standard cell potential (E°) we need to write oxidation and reduction half-reactions.
Oxidation: 2 H₂ ⇒ 4 H⁺ + 4 e⁻
Reduction: O₂ + 4 e⁻ ⇒ 2 O²⁻
The moles of electrons (n) involved are 4.
We can calculate E° using the following expression:
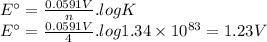
(b) Predict the signs of ΔH° and ΔS° for the fuel-cell reaction. ΔH°: positive negative ΔS°: positive negative
The standard Gibbs free energy is related to the standard enthalpy (ΔH°) and standard entropy (ΔS°) through the following expression:
ΔG° = ΔH° - T.ΔS°
Usually, the major contribution to ΔG° is ΔH°. So, if ΔG° is negative (exergonic), ΔH° is expected to be negative (exothermic).
The entropy is related to the number of moles of gases. There are 3 gaseous moles in the reactants and 0 in the products, so the final state is predicted to be more ordered than the initial state, resulting in a negative ΔS°.
(c) As temperature increases, does the maximum amount of work obtained from the fuel-cell reaction increase, decrease, or remain the same?
The maximum amount of work obtained depends on the standard Gibbs free energy.
wmax = ΔG° = ΔH° - T.ΔS°
Since ΔS is negative, as T increases, ΔG becomes more positive. Therefore, the maximum work obtained will decrease as T increases.