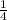Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Let "XB " represents the dominant allele for no baldness
and let "Xb " represents the recessive premature male-pattern baldness
Genotype of affected male is Xb Y
Genotype of heterozygous female XB Xb
Now when the above male and female are crossed, the following offspring are produced
Xb Y * XB Xb
XB Xb, XB Y, Xb Xb, Xb Y
Since, this Xb allele is only expressed in males, therefore females will not be affected by it
Hence, out of 4 offspring only one male offspring with "XbY" genotype will have premature baldness