Answer:
D is the correct representation.
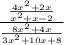 =
=
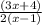
Explanation:
Here, the given equation is:
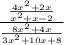
here, numerator =
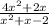
and denominator =
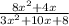
Solving numerator and denominator separately, we get
NUMERATOR:
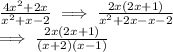
Denominator:
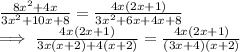
Hence, the transformed fraction is:
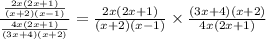
or, implied fraction is
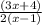
Hence, D is the correct representation.