Answer:
The metal was silver.
Step-by-step explanation:
We need to remember the equation for specific heat (C) that relate heat (Q), mass (m) and temperature (T) as:
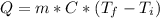 . Then we need to calculate for every single metal their change of temperature as:
. Then we need to calculate for every single metal their change of temperature as:
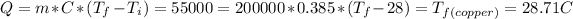 ,
,
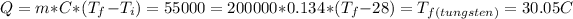 ,
,
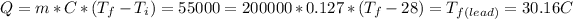 , and
, and
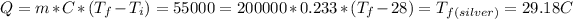 , so the last one it's the same temperature that was given to find and the metal was silver.
, so the last one it's the same temperature that was given to find and the metal was silver.