Answer:
The p-value becomes lower.
Explanation:
Let
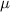 (unknown) be the true mean of number of hours of sleep each night. If we have the hypothesis
(unknown) be the true mean of number of hours of sleep each night. If we have the hypothesis
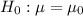 vs
vs
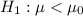 , the test statistic for a small sample size n = 20 is
, the test statistic for a small sample size n = 20 is
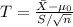 , where
, where
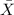 and S are the sample mean and standard deviation respectively. If
and S are the sample mean and standard deviation respectively. If
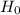 is true, we know that T has a t distribution with n-1 degrees of freedom. The p-value for the lower-tail alternative is computed as
is true, we know that T has a t distribution with n-1 degrees of freedom. The p-value for the lower-tail alternative is computed as
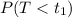 , where
, where
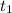 is the observed value for the given sample. If we increase the size of the sample and the sample mean and sample standard deviation stayed the same, then, the value
is the observed value for the given sample. If we increase the size of the sample and the sample mean and sample standard deviation stayed the same, then, the value
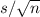 becomes smaller, besides, this quantity is always positive. The absolute value of
becomes smaller, besides, this quantity is always positive. The absolute value of
 stays the same, and the absolute value of the observed value
stays the same, and the absolute value of the observed value
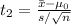 becomes bigger.
becomes bigger.
If
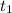 is negative, then,
is negative, then,
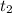 is also negative and smaller than
is also negative and smaller than
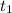 , therefore,
, therefore,
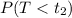 becomes lower.
becomes lower.