Answer:
Volume of hydrogen gas required for each volume of carbon dioxide is 3 times the volume of carbon dioxide gas.
Step-by-step explanation:
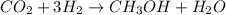
Volume of the carbon dioxide gas =
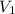
Temperature of the carbon dioxide gas =
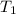
Pressure of the carbon dioxide gas =
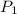
Moles of carbon dioxide gas =
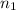
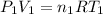 (ideal gas equation )
(ideal gas equation )
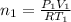 ..[1]
..[1]
Volume of the hydrogen gas =
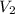
Temperature of the hydrogen gas =
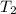
Pressure of the hydrogen gas =
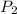
Moles of hydrogen gas =
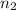
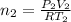 ..[2]
..[2]
According to reaction 1 mole of carbon dioxide reacts with 3 moles of hydrogen gas.
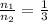
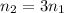
Using above value in [2]

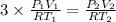
Given,

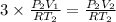
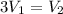
Volume of hydrogen gas = 3 × volume of carbon dioxide gas
Volume of hydrogen gas required for each volume of carbon dioxide is 3 times the volume of carbon dioxide gas.