Answer:
b.
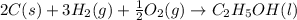
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, formation reactions are said to be undergone when only the elements constituting the involved compounds, react in order to yield it in a combination chemical reaction. In such a way, for ethanol, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen must react to form it. In addition, it is mandatory to remember that hydrogen and oxygen only exist diatomic as pure gaseous elements. Moreover, the reaction must be properly balanced therefore, ethanol's formation reaction turns out:
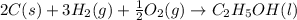
Which have an enthalpy of formation of -277.6 kJ/mol (exothermic reaction).
Best regards.