Answer:
The magnitude of force per unit length of one wire on the other is
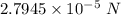 and the direction is away from one another
and the direction is away from one another
The magnitude of force per unit length of one wire on the other is
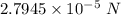 and the direction is towards each other.
and the direction is towards each other.
Step-by-step explanation:
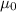 = Vacuum permeability =
= Vacuum permeability =
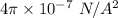
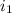 = Current in first wire = 2.9 A
= Current in first wire = 2.9 A
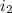 = Current in second wire = 5.3 A
= Current in second wire = 5.3 A
r = Gap between the wires = 11 cm
Force per unit length
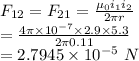
The magnitude of force per unit length of one wire on the other is
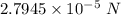 and the direction is away from one another
and the direction is away from one another
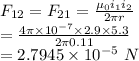
The magnitude of force per unit length of one wire on the other is
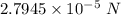 and the direction is towards each other.
and the direction is towards each other.