Answer:
D) Both chemical and the electrical gradients favor calcium entry into the cell.
Step-by-step explanation:
Naturally chemical gradient drives the movement of the chemical species, in this case Ca, from the regions of higher concentration to the regions of lower concentration. Then, Ca moves to inside the cell.
Whereas the movement due to electrical potential gradients is from higher to lower potentials for positive charges (negative charge move in opossite direction from lower to higher potentials). Calcium is a cation, it is positively charged
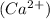 , so calcium would move to lower potentials, that is to more negative potentials. Then Ca moves to inside the cell.
, so calcium would move to lower potentials, that is to more negative potentials. Then Ca moves to inside the cell.