Answer:
The value of ΔG° of the reaction is 5704.82 J/mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
A + B ⇄ C + D
Equilibrium concentrations of reactants an products:
[A] = 10 μM, [B] = 15 μM, [C] = 3 μM, and [D] = 5 μM
An equilibrium constant of the reaction can be written as:
![K=([C][D])/([A][B])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/cvdk8zhyc3ifc00e24k06nxzx29bvranwi.png)
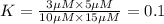
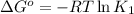
where,
R = Gas constant =
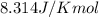
T = temperature =
![25^oC=[273+25]K=298K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/6roip9my7lmduj9zgvg2iw8f5svzc0eagc.png)
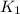 = equilibrium constant at 25°C = 0.1
= equilibrium constant at 25°C = 0.1
Putting values in above equation, we get:
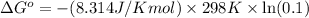
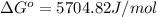
The value of ΔG° of the reaction is 5704.82 J/mol.