Answer:
The rate constant for the given reaction is
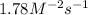 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
A + B → C + D
The initial concentrations of the reactants A = [A] = 0.400 M
The initial concentrations of the reactants B = [B] = 0.290 M
Order of reaction with respect to A = 1
Order of reaction with respect to B = 2
The rate of reaction = R = 0.060 M/s
The expression of the rate of the reaction will be given as:
![R=k[A]^1[B]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/xf23rqk6n4wnp58hr8sswuiirmqwwn6ftu.png)
![0.060 M/s=k[0.400 M]^1[0.290 M]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/r6cfu6d7dhn37f5cjgpep19muh77g5toap.png)
![k=(0.060 M/s)/([0.400 M]^1[0.290 M]^2)=1.78 M^(-2)s^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/t4hpwww0ex1xl97hmqsnhnd6kxqxj7huju.png)
The rate constant for the given reaction is
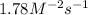 .
.