Answer:
Kgoal = 1.79x10⁻³³
Step-by-step explanation:
To form a global reaction by its steps, we may sum the steps reaction, multiply them for a constant value, or change them for the opposite reaction. If we do these operations, the constant of the equilibrium will change too. If we sum reactions, the constant resulting will be the multiplication of the constant of the reactions summed; if we multiply the reaction, the constant will be elevated by the constant; and if we change the reaction for the opposite, the constant will be inverted (1/K).
Let's first sum the reactions, if there is the same amount of one substance in the reactants and products, we may cancel it
N₂(g) + O₂(g) ⇄ 2NO(g) K1 = 4.10x10⁻³¹
N₂(g) + 2H₂(g) ⇄ N₂H₄(g) K2 = 7.40x10⁻²⁶
2H₂O(g) ⇄ 2H₂(g) + O₂(g) K3 = 1.06x10⁻¹⁰
--------------------------------------------------------------
2N₂(g) + 2H₂O(g) ⇄ 2NO(g) + N₂H₄(g) Kgoal = K1xK2XK3
Multipliying the reaction by 1/2:
N₂(g) + H₂O(g) ⇄ NO(g) + 1/2 N₂H₄(g) Kgoal =
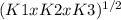
Kgoal = √K1xK2xK3
Kgoal = √(4.10x10⁻³¹x7.40x10⁻²⁶x1.06x10⁻¹⁰)
Kgoal = 1.79x10⁻³³