Answer:
(a)
vf₁ = (m₁*v₀₁+2m₂v₀₂- m₂v₀₁) / ( m₁+ m₂)
vf₂ = (v₀₁ - v₀₂ ) + ((m₁*v₀₁+2m₂v₀₂- m₂v₀₁) / ( m₁+ m₂))
(b)
vf₁ = - 3.367 m/s
vf₂ = 0.333 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Theory of collisions
Linear momentum is a vector magnitude (same direction of the velocity) and its magnitude is calculated like this:
p=m*v
where
p:Linear momentum
m: mass
v:velocity
There are 3 cases of collisions : elastic, inelastic and plastic.
For the three cases the total linear momentum quantity is conserved:
P₀ = Pf Formula (1)
P₀ :Initial linear momentum quantity
Pf : initial linear momentum quantity
Nomenclature
m₁ : mass of the first glider
m₂ : mass of the second glider
v₀₁:initial velocity of m₁
v₀₂ :initial velocity of m₂
vf₁: final velocity of m₁
vf₂: final velocity of m₂
Data
m₁,m₂,v₀₁i,v₀₂i
Problem development
(a) We appy the formula (1):
Because the initial and final velocities are in the same direction (i), (i) is canceled in the equation:
P₀ = Pf
m₁*v₀₁ + m₂*v₀₂ = m₁*vf₁ + m₂*vf₂ Equation( 1)
Because the shock is elastic, the coefficient of elastic restitution (e) is equal to 1.
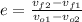
(equation 1)
vf₂ = (v₀₁ - v₀₂ ) + vf₁ Equation( 2)
We replace Equation( 2) in Equation( 1)
m₁*v₀₁ + m₂*v₀₂ = m₁*vf₁ + m₂* ((v₀₁ - v₀₂ ) + vf₁ )
m₁*v₀₁ + m₂*v₀₂ = m₁*vf₁ + m₂*v₀₁ - m₂ v₀₂ + m₂vf₁
m₁*v₀₁ + m₂*v₀₂ + m₂ v₀₂ - m₂*v₀₁= m₁*vf₁ + m₂vf₁
m₁*v₀₁+2m₂v₀₂- m₂v₀₁ = vf₁( m₁+ m₂)
vf₁ = (m₁*v₀₁+2m₂v₀₂- m₂v₀₁) / ( m₁+ m₂) Equation (3)
vf₂ = (v₀₁ - v₀₂ ) + vf₁
vf₂ = (v₀₁ - v₀₂ ) + ((m₁*v₀₁+2m₂v₀₂- m₂v₀₁) / ( m₁+ m₂)) Equation (4)
(b) Data
m₁, = 0.51 kg
m₂ = 0.98 kg
v₀₁,= 1.5 im/s
v₀₂ = -2.2 im/s
We replace data in the Equation (3) to calculate vf₁
vf₁ = (m₁*v₀₁+2m₂v₀₂- m₂v₀₁) / ( m₁+ m₂)
vf₁ = ( 0.51)* ( 1.5)+2 ( 0.98) ( -2.2) -(0.98) ( 1.5) / ( 0.51+ 0.98)
vf₁ = -3.367 m/s
We replace data in the Equation (2) to calculate vf₂
vf₂ = (v₀₁ - v₀₂ ) + vf₁
vf₂ = (1.5 -(-2.2 ) +(-3.367)
vf₂ = (1.5+2.2 ) -3.367
vf₂ = 0.333 m/s