Answer:
Null hypothesis: There is no statistically significant difference between our expected and observed values.
Degree of freedom: 1
Chi squared: 1.333
Null hypothesis is supported since our chi squared value is lower than our critical value, there are no statistically significant difference
Step-by-step explanation:
The Null hypothesis is a hypothesis that stipulates that there is no difference between the population being compared during statistical analyses/tests. Hence, in this case, the Null hypothesis posits that there is no significant difference between the expected and the observed phenotypic ratio.
Degree of freedom is calculated as n-1, where n = number of phenotypes in this case. Hence, Degree of freedom = 2 - 1 which is equal to 1.
Chi square (
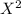 ) =
) =
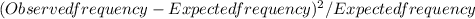
Since purple is dominant over white, the phenotype of the offspring should be 3:1 purple:white according to law of segregation. Hence, since there are 100 offspring in total;
Expected frequencies: purple 75, white 25
Observed frequencies: purple 70, white 30
(
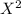 ) white =
) white =
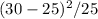 = 1
= 1
(
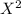 ) purple =
) purple =
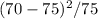 = 0.33
= 0.33
Hence, total (
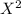 ) = 1.33
) = 1.33
The decision rule is such that;
- If calculated (
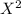 ) value is greater than critical value, the Null hypothesis is supported. If it is otherwise, the Null hypothesis is supported.
) value is greater than critical value, the Null hypothesis is supported. If it is otherwise, the Null hypothesis is supported.
In this case, the calculated (
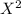 ) value is 1.33 and the critical value is 3.841, hence calculated value is less than the critical value. The Null hypothesis is supported.
) value is 1.33 and the critical value is 3.841, hence calculated value is less than the critical value. The Null hypothesis is supported.