Answer:
D
Explanation:
For any event A is always true
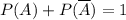
So, option A is true. From this equality,
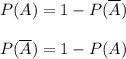
So, options B and C are true too.
Option D is not always true. The equality
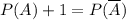
is true only for event A, for which
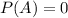
The equality
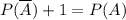
is true only for event A, for which
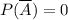
So, this option is not true for all events A.