Step-by-step explanation:
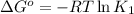
where,
R = Gas constant =
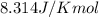
T = temperature =
![600^oC=[273.15+600]K=873.15 K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/andehdyr1fqv09t7ahzvvos58trsv9ei5n.png)
 = equilibrium constant at 600°C = 0.900
= equilibrium constant at 600°C = 0.900
Putting values in above equation, we get:
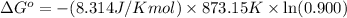
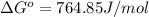
The ΔG° of the reaction at 764.85 J/mol is 764.85 J/mol.
Equilibrium constant at 600°C =
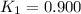
Equilibrium constant at 1000°C =
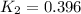
![T_1=[273.15+600]K=873.15 K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/o8o07bfm7bfgcuq97hywzlqmrvxph2agnu.png)
![T_2=[273.15+1000]K=1273.15 K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/5l1x7nydzidtv5d3cgnx79pukzx7ytzbk3.png)
![\ln (K_2)/(K_1)=(\Delta H^o)/(R)* [(1)/(T_1)-(1)/(T_2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/iq5bbl5cy8gbusj4ficgkwfq8ycysmzryd.png)
![\ln (0.396)/(0.900)=(\Delta H^o)/(8.314 J/mol K)* [(1)/(873.15 K)-(1)/(1273.15 K)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/klo0giqbth0o49q0o0jc6u6z5qcff7gve0.png)
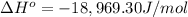
The ΔH° of the reaction at 600 C is -18,969.30 J/mol.
ΔG° = ΔH° - TΔS°
764.85 J/mol = -18,969.30 J/mol - 873.15 K × ΔS°
ΔS° = -22.60 J/K mol
The ΔS° of the reaction at 600 C is -22.60 J/K mol.
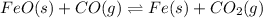
Partial pressure of carbon dioxide =
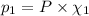
Partial pressure of carbon monoxide =
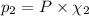
Where
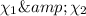 mole fraction of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide gas.
mole fraction of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide gas.
The expression of
 is given by:
is given by:
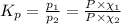
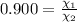
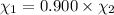
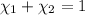
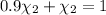
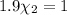
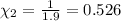
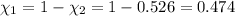
Mole fraction of carbon dioxide at 600°C is 0.474.