Answer:
4.945 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
- Based on Dalton's law of Partial pressure, the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equivalent to the sum of individual partial pressures of the gases in the mixture.
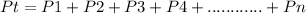
In this case;
Partial pressure of Oxygen, P(O) = 0.255 atm
Partial pressure of N, P(N) = 3.24 atm
Partial pressure of Ar, P(Ar) = 1.45 atm
Therefore;
P(total) = P(O) + P(N) + P(Ar)
= 0.255 atm + 3.24 atm + 1.45 atm
= 4.945 atm
Therefore, the total pressure of the mixture is 4.945 atm