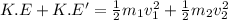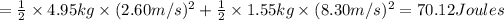Answer:
A) The speed of the water must be 8.30 m/s.
B) Total kinetic energy created by this maneuver is 70.12 Joules.
Step-by-step explanation:
A) Mass of squid with water = 6.50 kg
Mass of water in squid cavuty = 1.55 kg
Mass of squid =
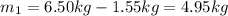
Velocity achieved by squid =
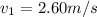
Momentum gained by squid =
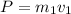
Mass of water =
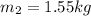
Velocity by which water was released by squid =
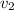
Momentum gained by water but in opposite direction =
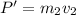
P = P'
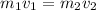
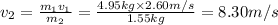
B) Kinetic energy does the squid create by this maneuver:
Kinetic energy of squid = K.E =
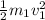
Kinetic energy of water = K.E' =
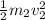
Total kinetic energy created by this maneuver: