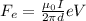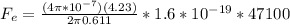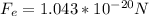Answer:
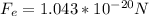
Step-by-step explanation:
To give a proper solution to this problem we need to apply the concept about Force on electron, which is given by,
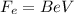
Where,
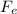 = Perpendicular Force to the direction of magnetic field
= Perpendicular Force to the direction of magnetic field
B = Magnetic field
V = Velocity (Perpendicular also)
We know that B is given by
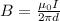
Where
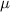 is the permeability constant I is the current and d the distance
is the permeability constant I is the current and d the distance
Replacing in the Force equation,