Answer:
A. The central bright fringe becomes wider.
Step-by-step explanation:
Width of central bright fringe is given by the formula
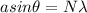
now for position of first minima on both sides of central bright fringe is given as
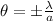
so the angular width of central maximum is given as
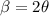
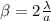
now width of maximum is given as
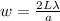
now we can see that this width is inversely depends on the width of slit
so on decreasing the slit width the central maximum width must have to increase