To solve this problem we need to consider the concept about Ampere's Law.
The Ampere's law say that,
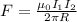
Where,
F= Mangetic field
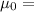 Permeability of free space
Permeability of free space
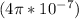
I =current
R= Radius from the wire in meters.
A) At the first case the force on wire is repulsive, replacing our values
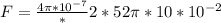
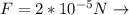 In repulsive direction.
In repulsive direction.
B) At the second case de Force flow in the same direction, then we have,
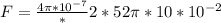
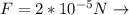 In attractive direction
In attractive direction