Answer: The radius of positive ion is smaller than the radius of an atom because of the increase of effective nuclear charge for the positive ion.
Step-by-step explanation:
Atomic radius of an atom is defined as the total distance from the nucleus to the outermost shell of the atom.
Effective nuclear charge is defined as the attraction of the protons present in the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electrons.
For ions, the effective nuclear charge changes than the neutral atom.
There are two types of ions:
- Cations: They are formed when an atom looses its valence electrons. They are positive ions.
- Anions: They are formed when an atom gain electrons in its outermost shell. They are negative ions.
For positive ions, the removal of electron increases the nuclear charge for an outermost electron because the outermost electrons are more strongly attracted by the nucleus. So, the effective nuclear charge increases for cations. This decreases the size of cation as compared to the neutral atom
For Example: Radius of
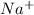 ion is less than the neutral Sodium (Na) atom
ion is less than the neutral Sodium (Na) atom
Hence, the radius of positive ion is smaller than the radius of an atom because of the increase of effective nuclear charge for the positive ion.