Solve the equations for y. If x lies at the numerator on the other side, then it's direct variation. If it lies at the denominator, its inverse variation.
For example, in the first equation, you have
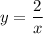
The equation is solved for y, and x is at the denominator, so this is an inverse variation.
As another example, if we solve the third equation for y (i.e. if we divide both sides by 4), we have

so again this is an inverse variation.
Apply this rule to all equations to tell whether they are direct, inverse or neither.