Answer:
To calculate the absolute pressure we used the depth as 2 m instead of 2 mm because the given dimensions for the swimming pool do not make sense (they are too small).
The absolute pressure on the bottom of a swimming pool is 1.21x10⁵ Pa.
Step-by-step explanation:
The absolute pressure is given by:
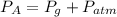
Where:
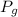 : is the gauge pressure
: is the gauge pressure
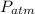 : is the atmospheric pressure = 1 atm = 101325 Pa
: is the atmospheric pressure = 1 atm = 101325 Pa
The gauge pressure can be found as follows:
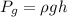
Where:
ρ: is the density of water = 1000 kg/m³
g: is the gravity = 9.81 m/s²
h: is the height or the depth
Since the given dimensions in the statement for the swimming pool do not make sense (they should be in meters instead of millimeters), we will use h = 2 m.
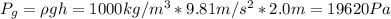
Hence, the absolute pressure is:
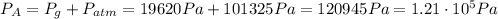
Therefore, the absolute pressure on the bottom of a swimming pool is 1.21x10⁵ Pa.
I hope it helps you!