Answer:
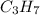
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
At first, based on the given information, one proceeds to compute the moles of carbon that the alkane has by considering the yielded amount of carbon dioxide as follows:
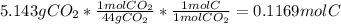
Next, the moles of hydrogen coming from the yielded water as:
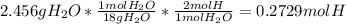
Now, dividing by the carbon's moles, one computes the empirical formula as follows:
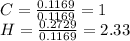
The closest whole-numbered factor, by multiplying by 3 is:
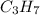
So it is its empirical formula which allows us to determine the molecular formula if needed which is:
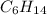
As it is twice the empirical formula.
Best regards.