Answer:
1.

2.
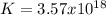
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
1.) By coupling the given reaction with the formation of carbon dioxide, one states the total reaction as:
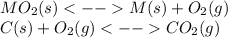
____________________________________

2.) Now, since we know that the Gibbs free energy for the decomposition of the metal is 288.5kJ/mol and the Gibbs free energy for the formation of carbon dioxide has a value of −394.39kJ/mol, the total Gibbs free energy for this process is:
Δ
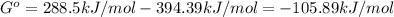
So the equilibrium constant is:
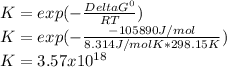
Best regards.