Answer:
P[(X=n+k)] ∩ X>n)] =P[X=K]
Explanation:
If X is a geometric random variable then
for success probability = p
so for failure q= 1-p
Now as given
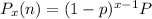
Now for the P parameter we have
x∈{1,2,3,....∞}
![P [X=K] = (1-P)^(K-1)P_{}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ostzy9ww5zko4wjpqb8vmqp6px43fu88px.png)
![P [X=n+K] = (1-P)^(n+K-1)P_{}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/high-school/kadubrchiqaglnze0jax3weuc629aarjfp.png)
![p[(X=n+K)/(X>h)]=([(X=n+K)n,X>n])/(P(X>n))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/high-school/67lg06axl68ye7ua3vswpt9fpujt2lyynk.png)
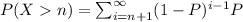
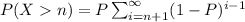
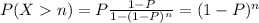
P[(X=n+k)] ∩ X>n)] = P(X=n+K)
P[(X=n+k)] ∩ X>n)] =
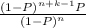
P[(X=n+k)] ∩ X>n)] =
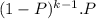
P[(X=n+k)] ∩ X>n)] =P[X=K]