Answer:
12) I = 800 kg m/ s , 13) Δv = 31.25 m / s, 14) F = -3600 N , 15) Δv = 4.44 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
In this strange exercise you are asked to answer a series of questions
12) force F = 800N applied mass m = 80 kg has a speed change of DV = 10 m / s, calculate the momentum
I = Δp
I = m Δv
I = 80 10
I = 800 kg m / s
13) a mass of m = 0.80 kg, has an impulse of 25 N s, determines the change in speed
I = m Δv
Δv = I / m
Δv = 25 / 0.8
Δv = 31.25 m / s
14) a mass m + 1200 kg is carried from 25 m / s to 10 m / s in a period of 5.0 s, determine the force
I = m (
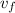 -v₀)
-v₀)
the proemd force for this impulse
I = F t
we substitute
F t = m (v_{f} -v₀)
F = m (v_{f} -v₀ / t
F = 1200 (10-25) / 5
F = -3600 N
the negative sign indicates that the force is in the opposite direction of the movement
15) a mass = 90 kg with velocity v = 9.0 m has a momentum of I = 400N s, determines the change in velocity
I = m Δv
Δv = I / m
Δv = 400/90
Δv = 4.44 m / s
if they asked for the final speed it would be.
I = m (v_{f} -v₀)
v_{f} = v₀ + I / m
v_{f} = 9 + 400/90
v_{f} = 13.4 m / s