Answer:
a) True
b) True
c) True
d) False
e) False
Explanation:
(a) All other factors remaining the same, increasing the sample size, n, will decrease the width of a confidence interval.
True. Confidence intervals are calculated by calculating margin of error (ME) around the mean using the formula
ME=
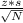 where
where
- z is the corresponding statistic (z-score or t-score)
- s is the standard deviation of the sample(or of the population if it is known)
- N is the sample size
As the formula suggests, all other factors remaining the same, if we increase N, ME decreases.
b) We expect 95% of all 95% confidence intervals for the population mean to contain the sample mean.
True. This is what 95% confidence level assumes.
(c) The t-distribution is symmetric and centered at the population mean
True.
(d) The t-distribution is very similar to the standard normal distribution regardless of its degrees of freedom.
False. As the degrees of freedom increases t-distribution resembles the standard normal distribution. For small sample sizes (<30), this is not true.
(e) All other factors remaining the same, a 90% confidence interval for a population mean is narrower than an 95% confidence interval for the same population
False. 90% confidence interval for a population mean is wider than an 95% confidence interval for the same population