Our data are,
State 1:

State 2:

We know as well that

To find the mass we apply the ideal gas formula, which is given by

Re-arrange for m,

Because of the pressure, temperature and volume ratio of state 1 and 2, we have to
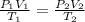
Replacing,

For conservative energy we have, (Cv = 0.718)
