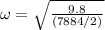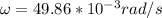Answer:
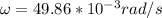
Step-by-step explanation:
We start converting to SI units,
A mile = 1609m
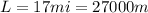
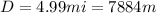
We know that the expression, which can relate linear acceleration and angular velocity is given by,
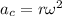
Where
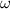 is the angular velocity
is the angular velocity
r=radius
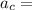 linear acceleration,
linear acceleration,
Re-arrange for \omega,
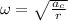
Our acceleration is equal to the gravity force, so replacing,