We have two events that occurred on different axes, the most convenient is to perform the operations on the two axes, and then look for the resulting force.
Our values are,
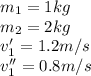
PAR A) For the X axis, we apply momentum conservation, which is given by,
Total momentum before = Total momentum After
We start from rest, so in X the initial speeds are 0,
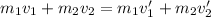
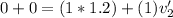
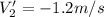
Now we apply for the conservation of the moment, it is part of the rest, so,
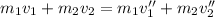
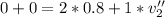
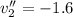
To find the total speed, we simply apply pitagoras,
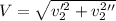
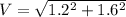
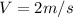
PART B) The address is given by,
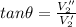
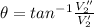
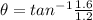
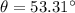 (Below -x axis)
(Below -x axis)