Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
The horizontal and vertical component of velocity of an electron is:
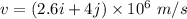
The magnetic field acting there is given by :
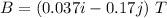
(a) The magnitude of the magnetic force on the electron is given by :
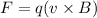
q = e
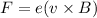
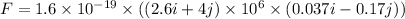
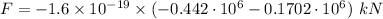
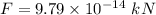
(b) We know that the charge on proton is :
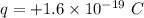
The magnetic force as same as for electron but the direction is opposite i.e.

Hence, this is the required solution.